Anti-aging skincare isn't about chasing youth—it's about maintaining healthy, resilient skin at every age. Here's what actually works, when to start, and how to build an effective routine.
When Should You Start Anti-Aging Skincare?
The Short Answer
Prevention should start in your 20s. Treatment can start whenever you notice changes.
The Science
- Collagen production decreases ~1% per year after age 25
- Sun damage accumulates from childhood
- Cell turnover slows starting in your late 20s
- Fine lines typically appear in your late 20s to early 30s
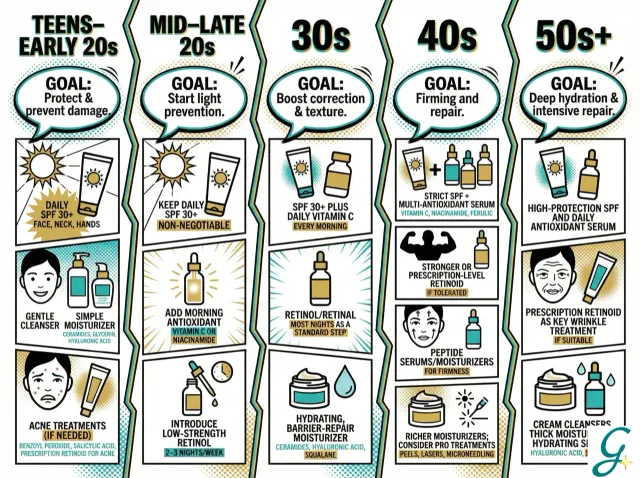
Age-Specific Recommendations
20s: Focus on prevention
- Sunscreen daily (most important)
- Antioxidants (vitamin C)
- Good basic routine
30s: Add treatment
- Start retinoids
- Eye cream
- More targeted serums
40s+: Intensify and maintain
- Stronger retinoids
- Peptides
- Consider professional treatments
What Actually Works: Evidence-Based Ingredients
Tier 1: Strong Scientific Evidence
Sunscreen
The single most effective anti-aging product:
- Prevents 90% of visible aging
- Protects against skin cancer
- Should be used daily, year-round
How to use: SPF 30+ broad-spectrum, every morning, reapply every 2 hours outdoors
Retinoids
The gold standard for treating aging:
- Increase cell turnover
- Boost collagen production
- Reduce fine lines and wrinkles
- Improve skin texture and tone
Types (weakest to strongest):
- Retinyl palmitate
- Retinol
- Retinaldehyde
- Adapalene (OTC)
- Tretinoin (prescription)
- Tazarotene (prescription)
How to use: Start low (0.25% retinol), use 2-3 nights/week, gradually increase
Vitamin C
Powerful antioxidant with multiple benefits:
- Protects against environmental damage
- Brightens skin
- Supports collagen synthesis
- Enhances sunscreen protection
Best form: L-ascorbic acid 10-20% How to use: Morning, before sunscreen
Tier 2: Good Evidence
Niacinamide
Versatile anti-aging ingredient:
- Strengthens skin barrier
- Reduces fine lines
- Improves skin tone
- Minimizes pores
How to use: 5-10%, morning and/or evening
Peptides
Signal skin to produce more collagen:
- Matrixyl (palmitoyl pentapeptide)
- Copper peptides
- Argireline
How to use: Found in serums and moisturizers, use as directed
AHAs (Glycolic, Lactic Acid)
Exfoliate and stimulate renewal:
- Remove dead skin cells
- Improve texture
- Boost radiance
- Enhance product absorption
How to use: 2-3 times per week, evening
Tier 3: Promising but Less Evidence
- Bakuchiol (natural retinol alternative)
- Resveratrol
- Coenzyme Q10
- Growth factors
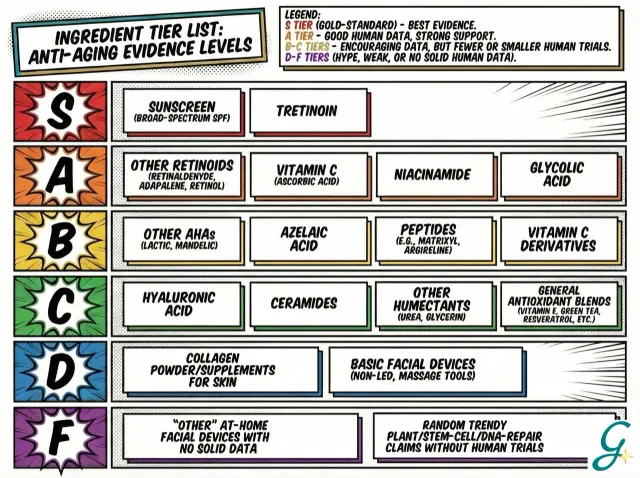
The Complete Anti-Aging Routine
Morning Routine
- Gentle Cleanser — Don't strip your skin
- Vitamin C Serum — Antioxidant protection
- Eye Cream — Target delicate eye area
- Moisturizer — Hydration and barrier support
- Sunscreen SPF 30+ — Non-negotiable
Evening Routine
- Double Cleanse — Remove sunscreen thoroughly
- Exfoliant (2-3x/week) — AHA or gentle retinol nights
- Retinoid (alternate nights) — Anti-aging treatment
- Eye Cream — Can use retinol eye cream
- Moisturizer/Night Cream — Support overnight repair
- Facial Oil (optional) — Seal in moisture
Anti-Aging Skincare for Sensitive Skin
Sensitive skin can still benefit from anti-aging ingredients with the right approach.
Gentle Retinoid Options
- Retinyl palmitate — Weakest, least irritating
- Encapsulated retinol — Slow release, less irritation
- Bakuchiol — Plant-based alternative, no irritation
- Granactive retinoid — Gentle synthetic retinoid
Sensitive Skin Tips
- Introduce one new product at a time
- Start with lowest concentrations
- Buffer retinoids (apply over moisturizer)
- Use every 3rd night initially
- Skip actives during flare-ups
- Prioritize barrier health
Soothing Ingredients to Pair With
- Centella asiatica
- Aloe vera
- Ceramides
- Panthenol
- Allantoin

Vegan Anti-Aging Skincare
Many effective anti-aging ingredients are naturally vegan or have vegan alternatives.
Vegan-Friendly Ingredients
- Vitamin C — Plant-derived
- Retinol — Can be synthetic (vegan) or animal-derived (check source)
- Bakuchiol — Plant-based retinol alternative
- Peptides — Synthetic, vegan
- Hyaluronic acid — Typically fermentation-derived (vegan)
- Niacinamide — Synthetic, vegan
- AHAs — Plant-derived
Ingredients to Watch
- Collagen — Usually animal-derived (look for plant-based alternatives or collagen-boosting ingredients)
- Retinol — Check if synthetic or animal-derived
- Squalane — Should be plant-derived (olive), not shark-derived
- Lanolin — Animal-derived, avoid
Building a Vegan Anti-Aging Routine
Focus on:
- Vitamin C (antioxidant, collagen support)
- Bakuchiol or vegan retinol (cell turnover)
- Peptides (collagen signaling)
- Niacinamide (barrier and anti-aging)
- Plant-derived squalane (hydration)
Best Clean Anti-Aging Skincare
"Clean beauty" prioritizes ingredients perceived as safer and more natural.
Clean Anti-Aging Ingredients
- Bakuchiol — Natural retinol alternative
- Vitamin C — Plant-derived antioxidant
- Rosehip oil — Natural source of vitamin A
- Plant peptides — Collagen support
- Green tea extract — Antioxidant
- Vitamin E — Natural antioxidant
What Clean Beauty Typically Avoids
- Synthetic fragrances
- Parabens
- Phthalates
- Formaldehyde releasers
- Certain silicones
Reality Check
"Clean" doesn't always mean more effective. Some synthetic ingredients (like retinoids) have stronger evidence than natural alternatives. Balance your values with efficacy.

Common Anti-Aging Mistakes
1. Starting Too Late
Prevention is easier than correction. Start sunscreen and antioxidants in your 20s.
2. Skipping Sunscreen
All anti-aging products are useless without sun protection. SPF daily, no exceptions.
3. Using Too Many Actives
Over-treating damages your skin barrier. Focus on a few proven ingredients.
4. Expecting Overnight Results
Anti-aging takes months to years. Be patient and consistent.
5. Neglecting Neck and Hands
These areas age too. Extend your routine beyond your face.
6. Ignoring Lifestyle Factors
Sleep, diet, stress, and exercise all affect skin aging.
Lifestyle Factors for Anti-Aging
Sleep
Skin repairs during sleep:
- Aim for 7-9 hours
- Sleep on your back
- Use silk pillowcase
Diet
Nutrition affects skin:
- Antioxidant-rich foods
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Limit sugar (glycation ages skin)
- Stay hydrated
Exercise
Regular movement:
- Increases circulation
- Reduces stress
- Promotes cellular health
Stress Management
Chronic stress accelerates aging:
- Increases cortisol
- Breaks down collagen
- Disrupts sleep
No Smoking
Smoking dramatically accelerates skin aging. If you smoke, quitting is the best anti-aging intervention.
Professional Anti-Aging Treatments
When products aren't enough:
- Chemical peels — Accelerated exfoliation
- Microneedling — Collagen induction
- Laser treatments — Resurfacing, tightening
- Botox — Prevent and treat expression lines
- Fillers — Restore volume
- RF/Ultrasound — Skin tightening
Consult a board-certified dermatologist for professional treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best anti-aging skincare routine?
An effective anti-aging routine includes: gentle cleanser, vitamin C serum (morning), moisturizer, SPF 30+ sunscreen (morning), and retinoid (evening). These four products—sunscreen, vitamin C, retinoid, and moisturizer—are the most evidence-backed anti-aging ingredients available.
At what age should you start anti-aging skincare?
Start sunscreen in childhood. Add antioxidants (vitamin C) in your early 20s for prevention. Introduce retinoids in your mid-20s to early 30s. However, it's never too late to start—your skin will benefit from anti-aging ingredients at any age.
What is the most effective anti-aging ingredient?
Sunscreen is the most effective because it prevents 80% of visible aging caused by UV damage. For treatment, retinoids (vitamin A derivatives) have the strongest evidence for reducing wrinkles, improving texture, and boosting collagen. Vitamin C provides antioxidant protection and brightening.
Do anti-aging products really work?
Yes, products with proven ingredients work when used consistently. Retinoids, vitamin C, niacinamide, peptides, and sunscreen all have scientific evidence supporting their anti-aging benefits. Results take 2-3 months to become visible and require ongoing use to maintain.
What is the difference between retinol and retinoid?
Retinoid is the umbrella term for all vitamin A derivatives. Retinol is a specific type of retinoid available over-the-counter—it's gentler but must convert to retinoic acid in skin. Prescription retinoids (tretinoin) are stronger and work faster but cause more irritation initially.
How long does it take to see anti-aging results?
Expect: 2-4 weeks for improved hydration and glow, 4-8 weeks for texture improvement, 2-3 months for visible reduction in fine lines, and 6-12 months for significant wrinkle improvement. Anti-aging is a long-term commitment—consistency over years yields the best results.
Track Your Anti-Aging Journey
Anti-aging is a long-term commitment. Results are gradual and easy to miss without documentation.
Glimmer helps you:
- Stay consistent with your routine
- Track which products work
- Document progress with photos
- Build lasting skincare habits
Sources
- Hughes, M. C. B., et al. (2013). "Sunscreen and Prevention of Skin Aging: A Randomized Trial." Annals of Internal Medicine, 158(11), 781-790.
- Mukherjee, S., et al. (2006). "Retinoids in the treatment of skin aging: an overview of clinical efficacy and safety." Clinical Interventions in Aging, 1(4), 327-348.
- Farris, P. K. (2005). "Topical Vitamin C: A Useful Agent for Treating Photoaging and Other Dermatologic Conditions." Dermatologic Surgery, 31, 814-818.
