Skin blemishes affect nearly everyone at some point. Whether you're dealing with dark spots, acne marks, or uneven patches, understanding what causes blemishes is the first step to treating them effectively.
What Are Skin Blemishes?
Skin blemishes are any marks, spots, or imperfections that differ from your normal skin tone or texture. They can be temporary or long-lasting, and range from barely noticeable to prominent.
Common types of skin blemishes include:
- Dark spots (hyperpigmentation)
- Acne and acne scars
- Age spots
- Melasma
- Sun spots
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH)
- Redness and rosacea
- Uneven skin tone
What Causes Skin Blemishes?
1. Sun Exposure
UV radiation triggers excess melanin production, leading to dark spots and uneven pigmentation. Sun damage accumulates over time, making sun protection essential.
2. Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy, birth control, and hormonal fluctuations can cause melasma—patches of darker skin, typically on the face.
3. Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
After acne, cuts, or skin inflammation, the skin often produces excess melanin during healing, leaving dark marks behind.
4. Aging
As skin ages, cell turnover slows and sun damage becomes more visible, resulting in age spots and uneven tone.
5. Genetics
Some people are more prone to hyperpigmentation and blemishes due to their genetic makeup and skin type.
How to Get Rid of Skin Blemishes
Prevention First
The best treatment is prevention. Protect your skin from further damage:
- Wear SPF 30+ daily — Even on cloudy days
- Avoid picking at skin — This causes PIH
- Treat acne early — Prevent scarring before it happens
- Wear hats and seek shade — Physical sun protection helps
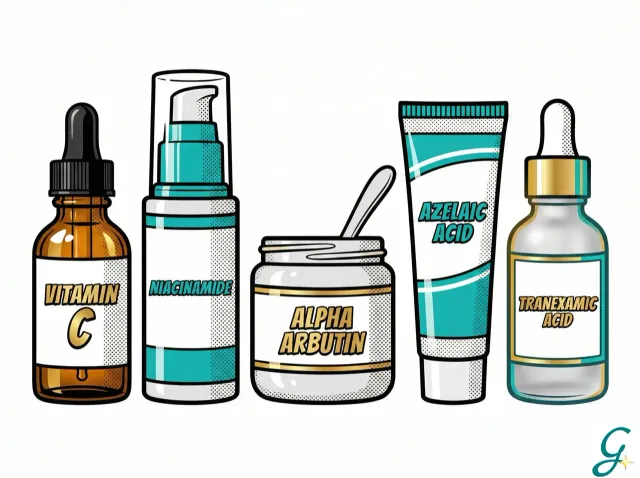
Effective Ingredients for Blemishes
Vitamin C
A powerful antioxidant that inhibits melanin production and brightens existing dark spots. Use a 10-20% L-ascorbic acid serum in the morning.
Best for: Prevention, brightening, overall radiance
Niacinamide
Vitamin B3 reduces melanin transfer to skin cells and strengthens the skin barrier. It's gentle enough for daily use.
Best for: Sensitive skin, redness, uneven tone
Alpha Arbutin
A gentle alternative to hydroquinone that inhibits tyrosinase (the enzyme that produces melanin).
Best for: Stubborn dark spots, melasma
Retinoids
Increase cell turnover, bringing fresh skin to the surface faster. Prescription tretinoin is most effective, but OTC retinol works too.
Best for: Anti-aging, texture, stubborn pigmentation
AHAs (Glycolic, Lactic Acid)
Chemical exfoliants that remove dead skin cells and fade surface pigmentation.
Best for: Dull skin, mild hyperpigmentation, texture
Azelaic Acid
Reduces melanin production and has anti-inflammatory properties. Safe for pregnancy and sensitive skin.
Best for: Acne marks, rosacea, melasma
Tranexamic Acid
Newer ingredient that's highly effective for melasma and stubborn pigmentation.
Best for: Hormonal pigmentation, melasma

How to Remove Skin Blemishes: A Step-by-Step Routine
Morning Routine
- Gentle cleanser — Don't strip your skin
- Vitamin C serum — Antioxidant protection and brightening
- Moisturizer — Hydrated skin heals better
- Sunscreen SPF 30+ — Non-negotiable for treating blemishes
Evening Routine
- Double cleanse — Remove sunscreen and impurities
- Exfoliant (2-3x/week) — AHA or gentle retinol
- Treatment serum — Niacinamide, alpha arbutin, or azelaic acid
- Moisturizer — Support skin barrier
Weekly Treatment
Consider adding a brightening mask or gentle peel once a week for accelerated results.
Professional Treatments for Stubborn Blemishes
When at-home treatments aren't enough, dermatologists offer:
- Chemical peels — Professional-strength exfoliation
- Laser treatments — Target pigmentation precisely
- Microneedling — Stimulates collagen and fades scars
- IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) — Treats sun damage and redness
- Prescription hydroquinone — Strongest topical for pigmentation
Always consult a dermatologist before pursuing professional treatments, especially for darker skin tones which require specialized approaches.
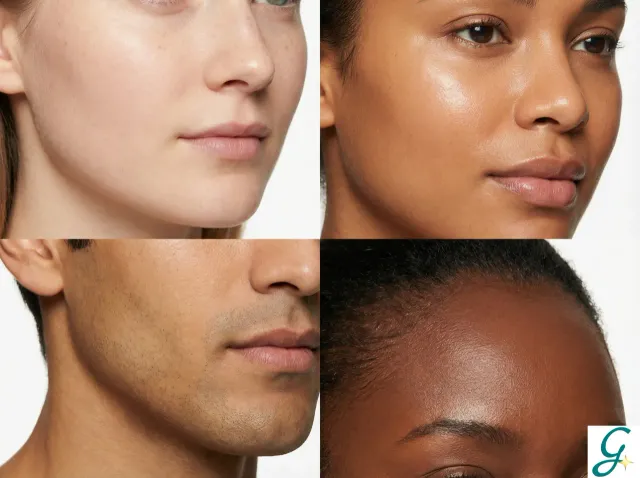
Blemish Treatment by Skin Tone
Different skin tones respond differently to treatments:
Fair Skin
- More prone to redness and sun damage
- Responds well to most treatments
- Higher risk of irritation from strong actives
Medium Skin
- Balanced approach works well
- Watch for PIH from aggressive treatments
- Consistent sunscreen is crucial
Olive and Deeper Skin Tones
- Higher risk of PIH from inflammation
- Avoid aggressive treatments that cause irritation
- Gentle, consistent approach is best
- Some laser treatments require specialized settings

Common Mistakes When Treating Blemishes
1. Skipping Sunscreen
Sun exposure darkens existing blemishes and creates new ones. No treatment works without sun protection.
2. Over-Exfoliating
Too much exfoliation causes inflammation, which leads to more pigmentation. Start slow.
3. Expecting Overnight Results
Blemishes take weeks to months to fade. Consistency over time is key.
4. Using Too Many Actives
Layering multiple strong ingredients causes irritation. Introduce one new product at a time.
5. Picking at Skin
Every time you pick, you risk creating new PIH. Hands off!
How Long Does It Take to Fade Blemishes?
Realistic timeline with consistent treatment:
- Surface discoloration: 4-8 weeks
- Post-acne marks: 2-6 months
- Deep pigmentation: 6-12 months
- Melasma: Ongoing management
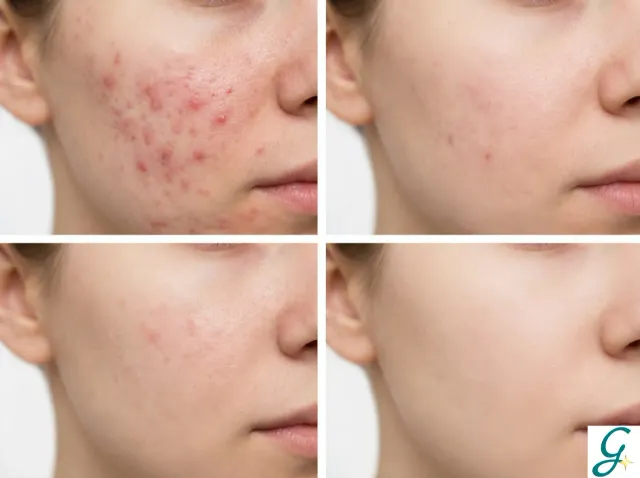
Patience and consistency are essential. Take progress photos to track improvement you might not notice day-to-day.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes skin blemishes?
Skin blemishes are caused by sun exposure (triggering excess melanin), post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from acne or injuries, hormonal changes (causing melasma), aging (slower cell turnover), and genetics. UV damage is the most common cause, which is why sunscreen is essential for both prevention and treatment.
How do I get rid of dark spots on my face?
Use a combination of vitamin C (brightening), niacinamide (reduces melanin transfer), alpha arbutin (inhibits pigment production), and retinoids (increases cell turnover). Apply sunscreen SPF 30+ daily—without it, no treatment will work effectively. Expect 2-6 months for visible improvement.
What is the fastest way to remove blemishes?
While there's no overnight fix, the fastest approach combines daily vitamin C serum, consistent sunscreen use, and regular exfoliation with AHAs. Professional treatments like chemical peels or laser therapy can accelerate results. Surface discoloration may fade in 4-8 weeks; deeper pigmentation takes 3-6 months.
Can blemishes be permanently removed?
Many blemishes can be significantly faded or eliminated with consistent treatment, but prevention is key to keeping them away. Sun exposure can bring back pigmentation, so ongoing sunscreen use is essential. Melasma often requires lifelong management as it can recur with hormonal changes or sun exposure.
Is vitamin C or niacinamide better for dark spots?
Both are effective but work differently. Vitamin C inhibits melanin production and provides antioxidant protection—best for prevention and brightening. Niacinamide reduces melanin transfer to skin cells and is gentler. For best results, use both: vitamin C in the morning, niacinamide morning or evening.
Why are my dark spots getting darker?
Dark spots darken with sun exposure, inflammation from over-exfoliating or harsh products, and hormonal changes. If you're treating blemishes without wearing sunscreen, UV exposure will counteract your efforts and make pigmentation worse. Always use SPF 30+ daily.
Track Your Blemish Treatment Progress
Fading blemishes requires consistent treatment over months. Tracking helps you:
- Stay consistent with your routine
- Document improvement with photos
- Identify which products work best
- Avoid products that cause irritation
Glimmer's photo journal feature lets you track your skin's progress over time, so you can see the results of your consistent efforts.
Sources
- Sarkar, R., et al. (2013). "Cosmeceuticals for Hyperpigmentation: What is Available?" Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery, 6(1), 4-11.
- Pullar, J. M., Carr, A. C., & Vissers, M. C. M. (2017). "The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health." Nutrients, 9(8), 866.
- Bissett, D. L., et al. (2005). "Niacinamide: A B Vitamin that Improves Aging Facial Skin Appearance." Dermatologic Surgery, 31, 860-865.
